Mounting Procedures and Examples of Damage
Furthermore, the maximum static load that bearings can withstand is shown in the NTN catalog as the bearing's “basic static load rating.” This is the maximum amount of force which can be applied to the central contact area between rolling elements and raceway surfaces. If exceeded, total permanent deformation exceeding 1/10,000 of the bore diameter will result, and smooth bearing rotation will be impaired. This is the basis for establishing the basic static load ratings.
Examples of Damage
 Flaking
Flaking
 Imbedding of solid contaminants
Imbedding of solid contaminants
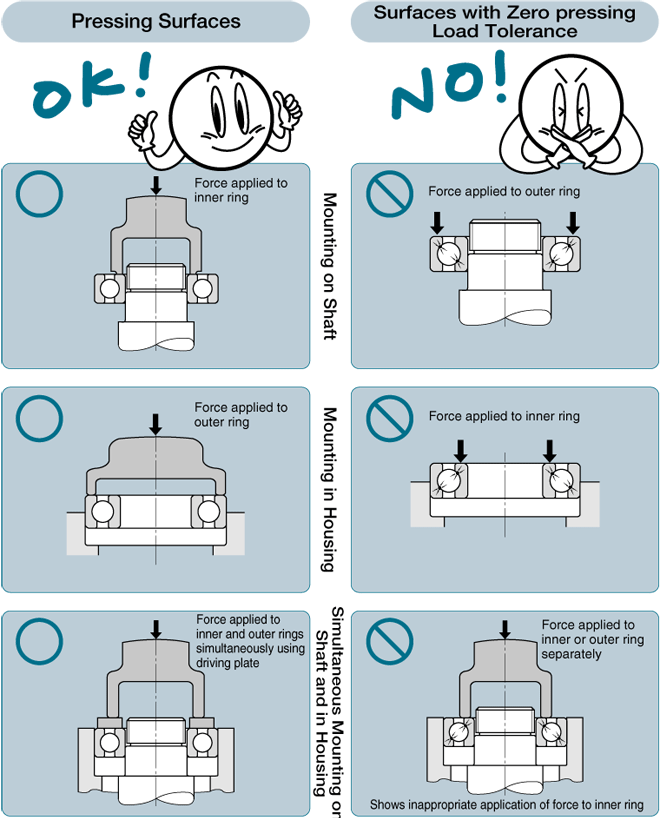
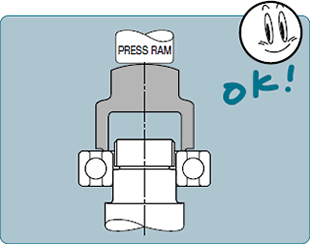
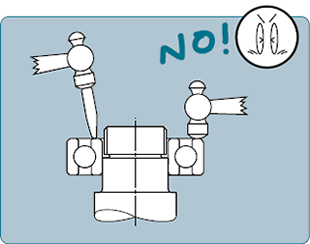
★ Mounting bearings using a hammer causes damage due to sharp impacts. Please mount press fit bearings using a pressing arbor or other designed to provide a uniform face.
Bearing Care

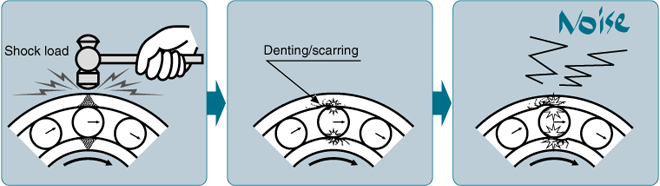
■Bearings are very susceptible to impacts and shock loads!
Bearings carry their loads along an extremely narrow contact surface between the rolling elements and the inner and outer raceway surfaces.
If an excessive load or impact is applied to this narrow area of contact, brinelling and/or scarring will occur. This damage leads to objectionable noise and vibration levels and rough bearing rotation. (Even dropping bearings on the floor will cause this type of damage.)
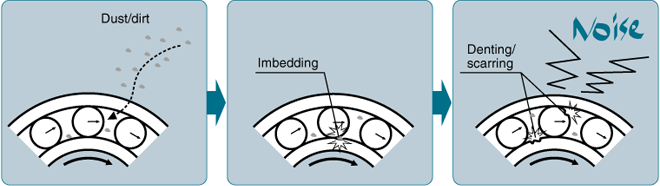
■Bearings are very susceptible to foreign particle contamination!
If foreign particles infiltrate the bearing during rotation, denting and/or scarring will occur and this will lead to poor bearing rotation and excess noise.
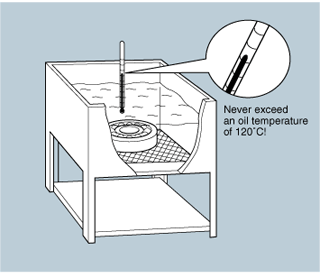
Temperature Mounting (Heat expansion of inner ring to ease installation)
 Heating temperature
Heating temperature
Commonly used for large bearings and bearings with a heavy interference fit.
- Immersion of the bearing in heated oil is the most common method.Use clean oil and suspend the bearing in the oil with a wire or support it underneath using a metal screen in order to avoid uneven heating of bearing elements.
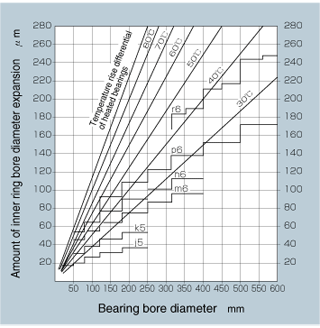
- The temperature to which the inner ring should be heated depends upon the amount of interference fit i.e. the diameter of the interference fit surfaces. Refer to the following graph to determine the proper temperature.
- To prevent gaps from occurring between the inner ring and shaft shoulder, bearings which have been heated and mounted on the shaft should be held in place until they have cooled completely.
■Observe these precautions when heating bearings
- Bearings should never be heated over 120°C.
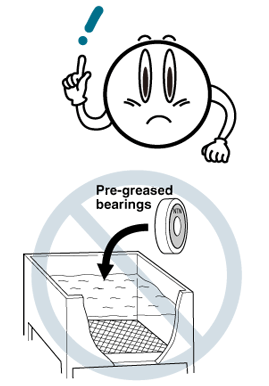
- This temperature mounting method cannot be used for pre-greased and sealed bearings or shielded bearings.
Other heating methods
 Bearing Oven
Bearing Oven
- Bearing Oven
Bearings are dry. This method can also be used for pre-greased bearings.
★When using this method with pre-greased bearings, do not heat the bearings above 120°C - Induction Heating
This method can also be used for the inner rings of cylindrical roller bearings. Bearings are dry and can be heated up in a short period of time.
After using this method, administer a demagnetizing treatment to the bearing. For more detailed information concerning bearing heating methods,contact NTN.
* Click here for Handling of Bearing Units.
https://www.ntnglobal.com/en/products/bearingunit/handling.html
