
Better Performance and More Compact and Lighter Weight “Rear-wheel Independent Steering System”May 21, 2015
[Improving vehicle driving performance and contributing to development of autonomous driving technology]
NTN Corporation (hereafter, NTN) announced the “Rear-wheel Independent Steering System*1” that utilizes steer-by-wire*2 technology for its steering system for electronically-controlled steering in 2013, and has made further enhancements for even better responsiveness and a more compact, lighter weight design.
Rear-wheel steering in automobiles is a function to assist vehicle stability at high speeds, as well as improve cornering at low to medium speeds, and electric actuators are used to drive the rear-wheel steering. “Left-right combined-type steering” systems that steer with a single actuator have no function for individual left-right toe angle control, while “left-right independent” systems with separate actuators mounted on each of the left and right wheels suffered from issues related to driving performance due to an increase in unsprung weight of vehicles.
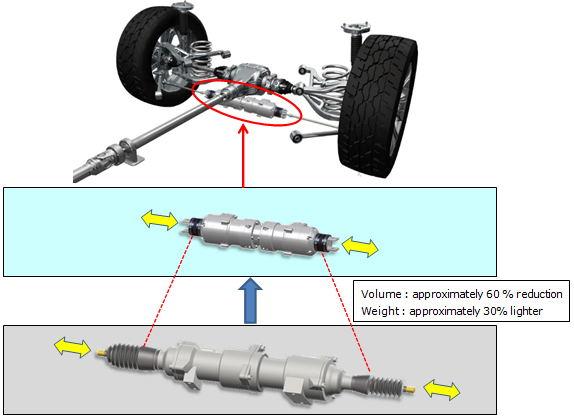
NTN's “Rear-wheel Independent Steering System” is capable of left-right toe angle control while consisting of a left-right combined-type steering layout, with no increase in the unsprung weight by mounting the actuator on the vehicle body. The enhanced product improves the steering speed up to a maximum of 10°/second (conventional product: 6°/second) to improve response with the vehicle's behavior during high-speed driving, avoiding emergencies or other situations. Increasing the tire's maximum steering angle to a wide range of ±2.5°*3 means a smaller minimum turning radius and lower driving stress when parking or driving, and is also anticipated to contribute to the future of autonomous driving technology.
The enhanced product also retains a similar level of rigidity as the conventional product with approximately 60% less volume and approximately 30% lighter weight to improve ease-of-mounting to vehicles. Mounting the enhanced product to vehicles as a left-right combined-type system does not affect ride comfort as there is no increase in unsprung weight.
NTN exhibits the system at the “Automotive Engineering Exposition 2015” automotive technology exposition being held at Pacifico Yokohama from May 20 to 22. Development will continue being made of module products that contribute to the electrification of vehicles, increase fuel efficiency and improve driving performance. Proposals will also be made with a view of covering the industrial machinery field, including construction machinery and agricultural machinery.
- 2011 Press release:
https://www.ntnglobal.com/en/news/new_products/news201100028.html - 2013 Press release:
https://www.ntnglobal.com/en/news/new_products/news201300104.html - The steering angle is determined by the design of the vehicle the system is mounted to, so reference figures have been listed.
Features
| (1) | Maximum steering speed 10°/second, maximum steering angle ±2.5° |
|---|---|
| (2) | Same level of rigidity as conventional product (axial force 7 KN), volume: approximately 60% reduction, weight: approximately 30% lighter |
| (3) | No increase in unsprung weight with the “left-right combined-type” system |
Applications
Automotive rear-wheel steering systems and the industrial machinery field including construction machinery and agricultural machinery
Inquiries about this release
Product photo
Rear-wheel Independent Steering System
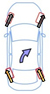
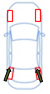
Effects of rear-wheel control
| Same Direction | Opposite Direction | Toe-in | Toe Angle 0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steering Condition | 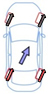 |
 |
 |
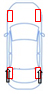 |
| Effect | Limits yaw that is generated when steering, and increases vehicle stability. | Reducing the minimum turning radius improves steering response at low speeds. | Improves straight-line performance in conditions such as crosswinds. | Improves fuel efficiency by reducing driving resistance. |
